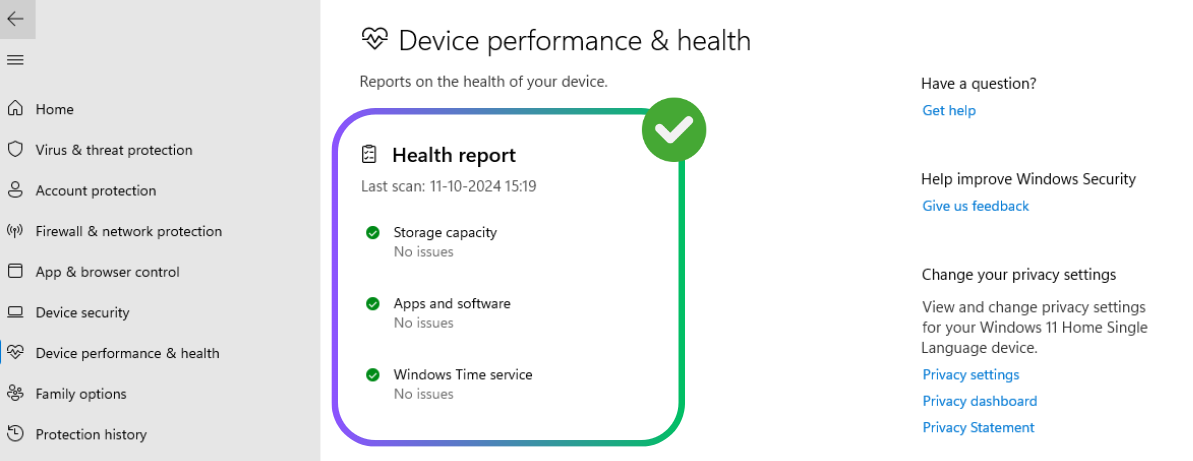
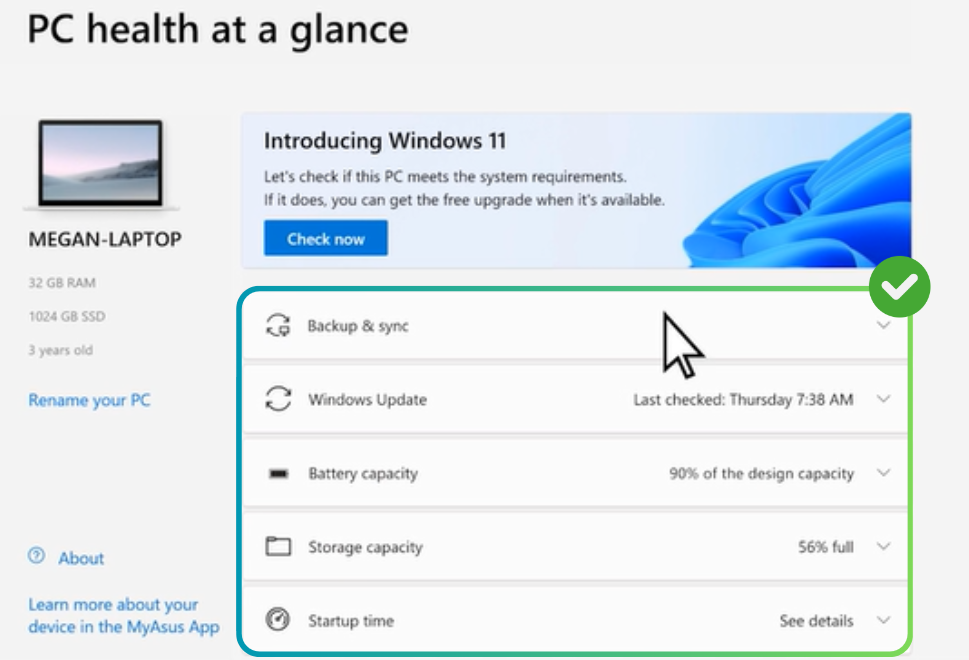
How to Check PC Health for Windows 11
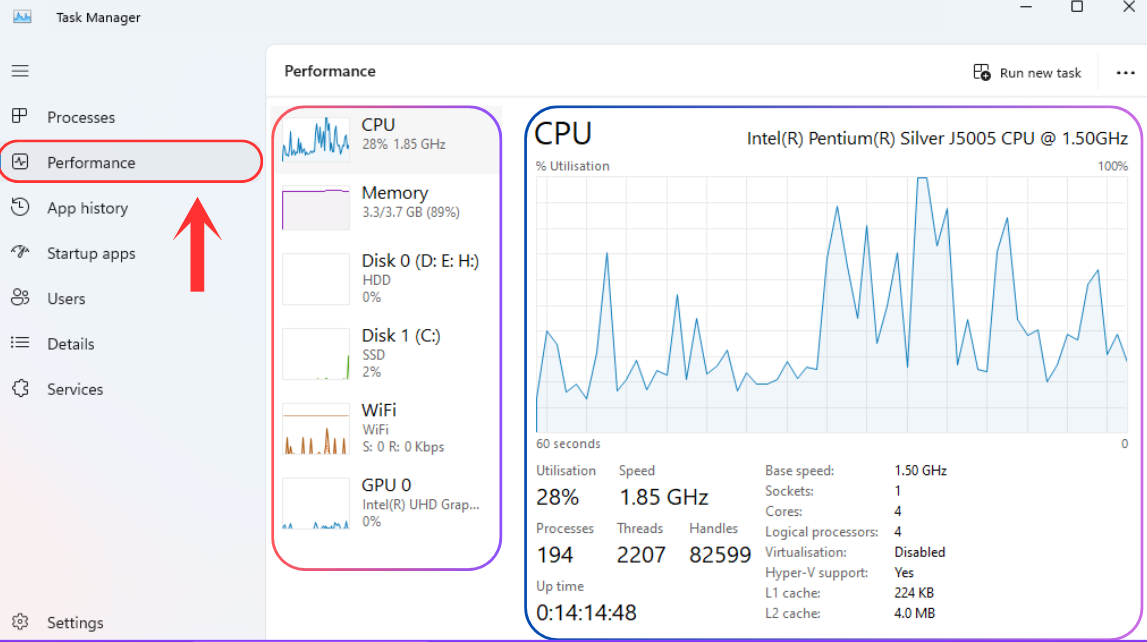
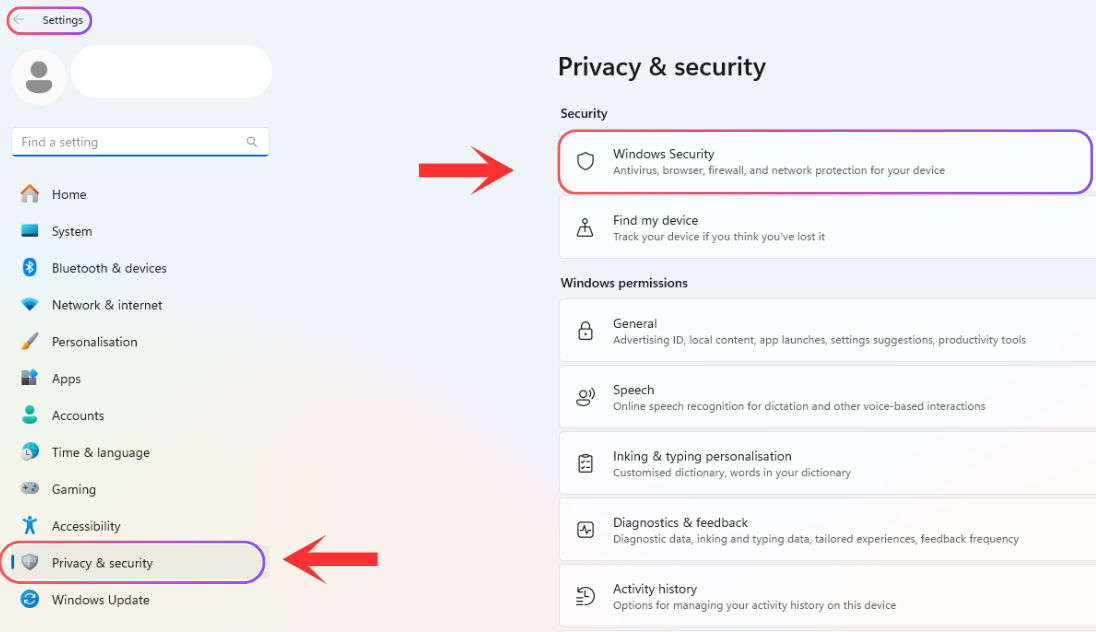
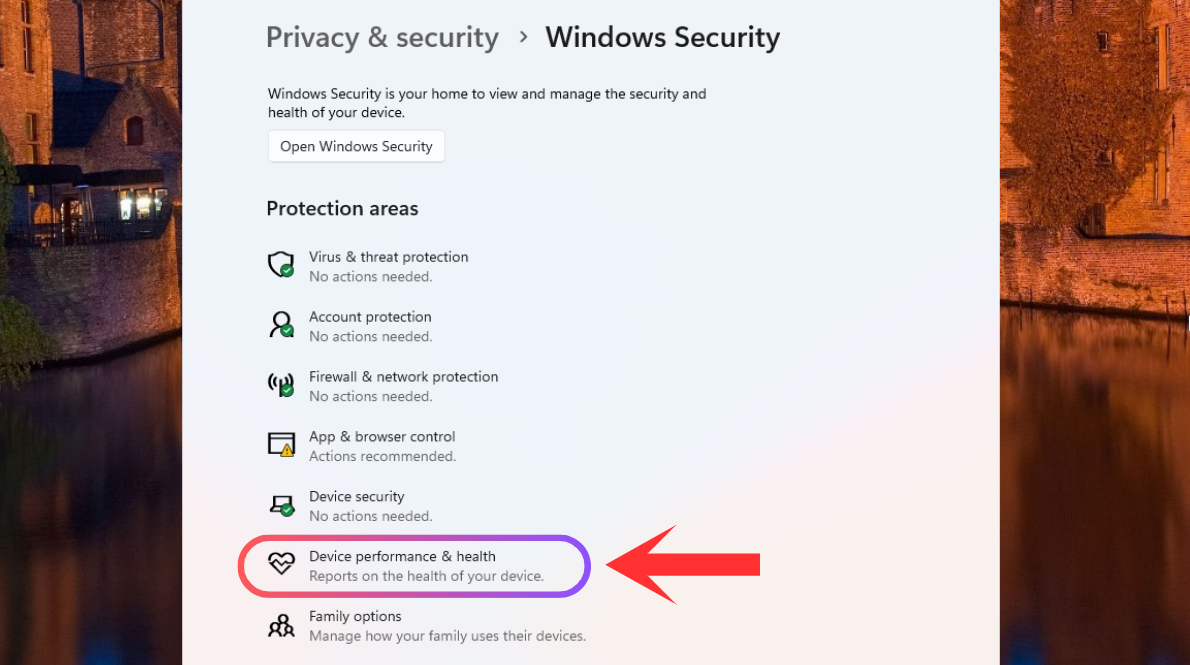
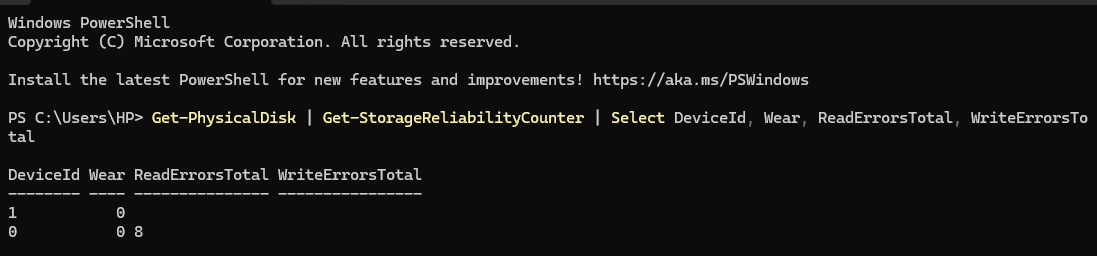
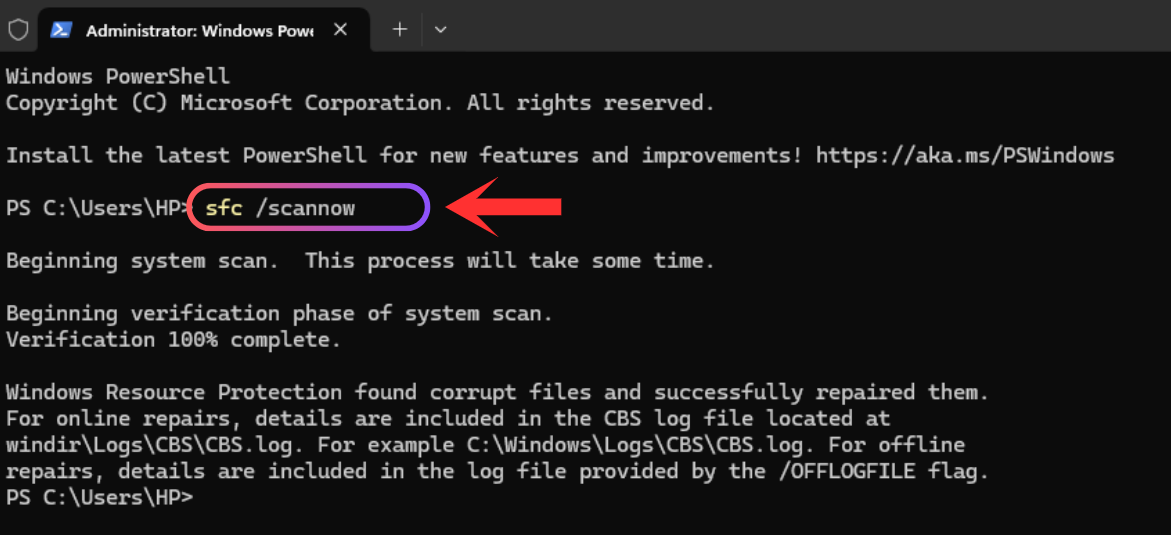
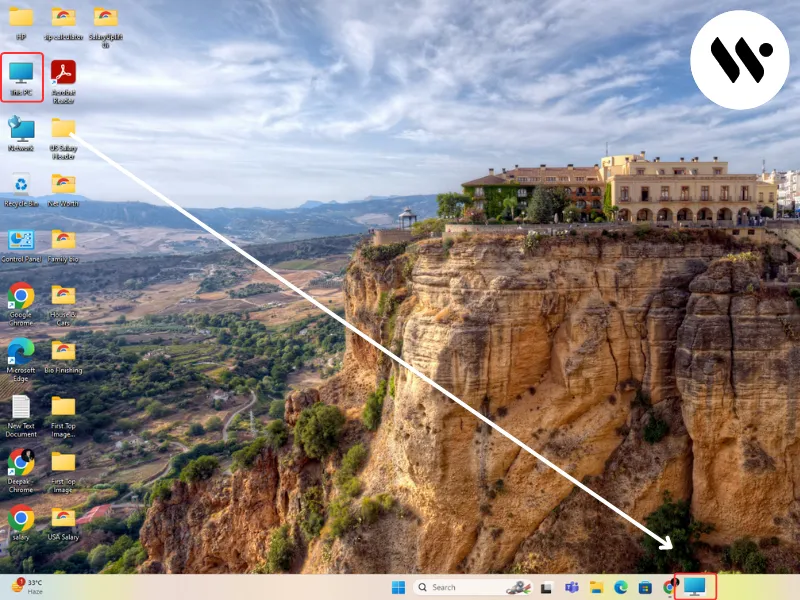
To keep your PC healthy and ensure smooth performance on Windows 11, it's important to take care of its health. You can use various tools to check your PC status, such as Task Manager, Windows Settings, PowerShell for SSDs, and the PC Health App. Check out working methods and tips to monitor your PC health.






.webp)






